It’s a bit slower than sleep mode, as it saves the system state onto your system drive rather than RAM, but it’s still a great way to extend battery life on Windows 11 — especially for laptops. Unfortunately, it’s not enabled by default on most Windows 11 systems.
Hibernate vs sleep mode on Windows 11
Which power-saving feature is better?
There are a lot of laptops with great battery life these days, but when you spend a lot of time on your laptop away from the charger, battery endurance is still a common concern. The power management features in Windows 11 can help out a bit, but you need to be familiar with how they work to use them effectively.
Putting your laptop or desktop PC in sleep mode saves the current system state, which includes open documents and any running apps. The system state is saved to RAM, and your computer enters a low-power state. It’s ideal for short breaks, as you can quickly pick up where you left off. Just keep in mind that sleep mode still sips a small amount of battery life. If your battery drains completely in this mode, you could lose your unsaved work.
On the other hand, hibernate mode saves your current system state to a hard drive or SSD and shuts down your system. The only difference between a normal shutdown and hibernate mode is that a normal shutdown does not save your system’s state. Unlike sleep mode, your system won’t use any power in hibernate mode. The next time you turn on your PC, you’ll see your apps and open documents just as you left them.
However, the downside is that waking up from hibernate takes longer than from sleep mode. This is because the system needs to reload the saved state from a slower hard drive or SSD rather than from the faster RAM.
How to enable hibernate mode in Windows 11 using Control Panel
The fastest way to enable hibernate mode in Windows 11 is by using the power options menu in the Control Panel.
- Launch the Start menu and search for Control Panel.
- From the Control Panel menu, click Hardware and Sound.
- Under Power Options, click Change what the power buttons do.
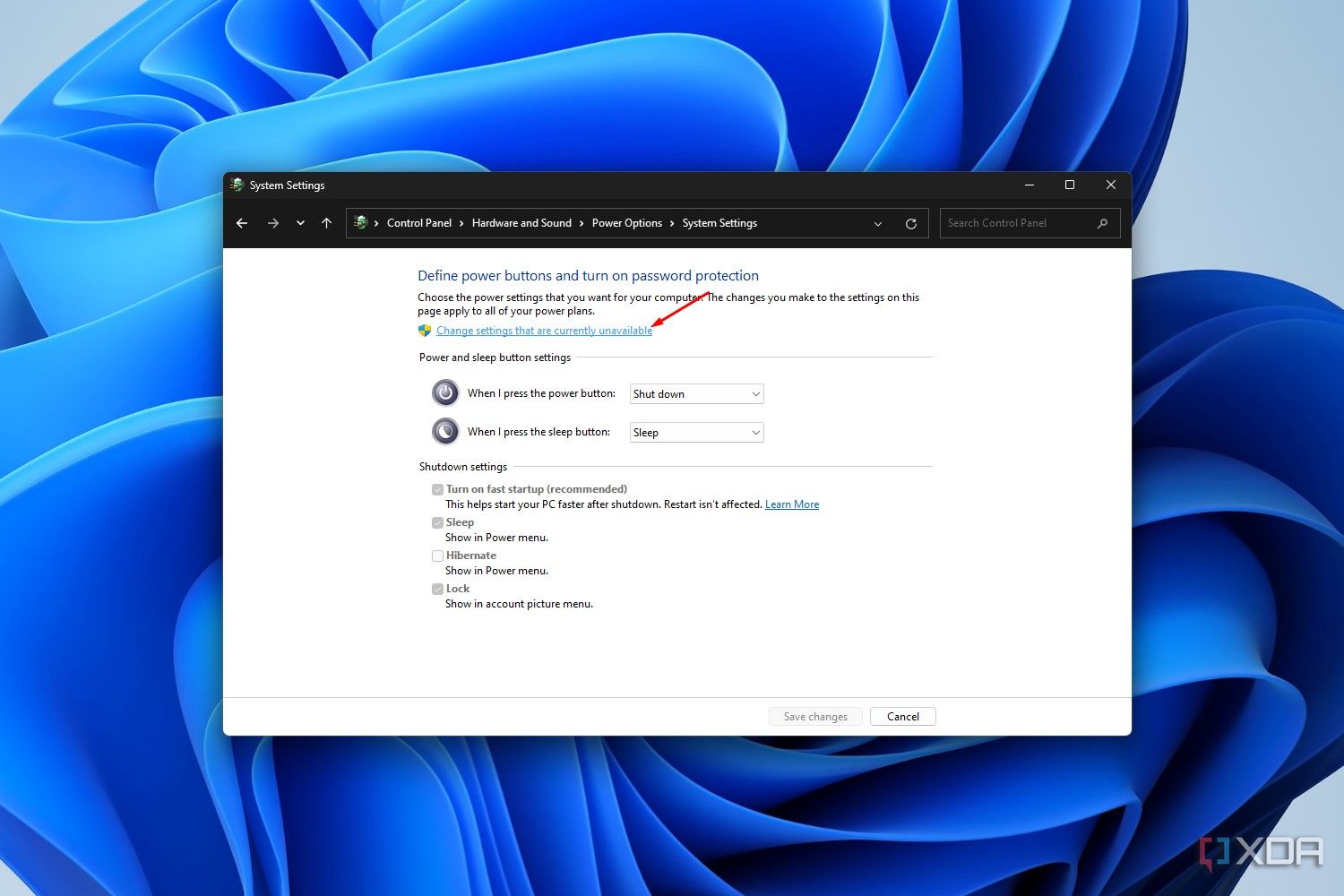
- You’ll see the Hibernate option at the bottom, but it’s likely grayed out. Click Change settings that are currently unavailable to interact with the grayed-out settings.
- Tick the box next to the Hibernate setting, and click Save changes.
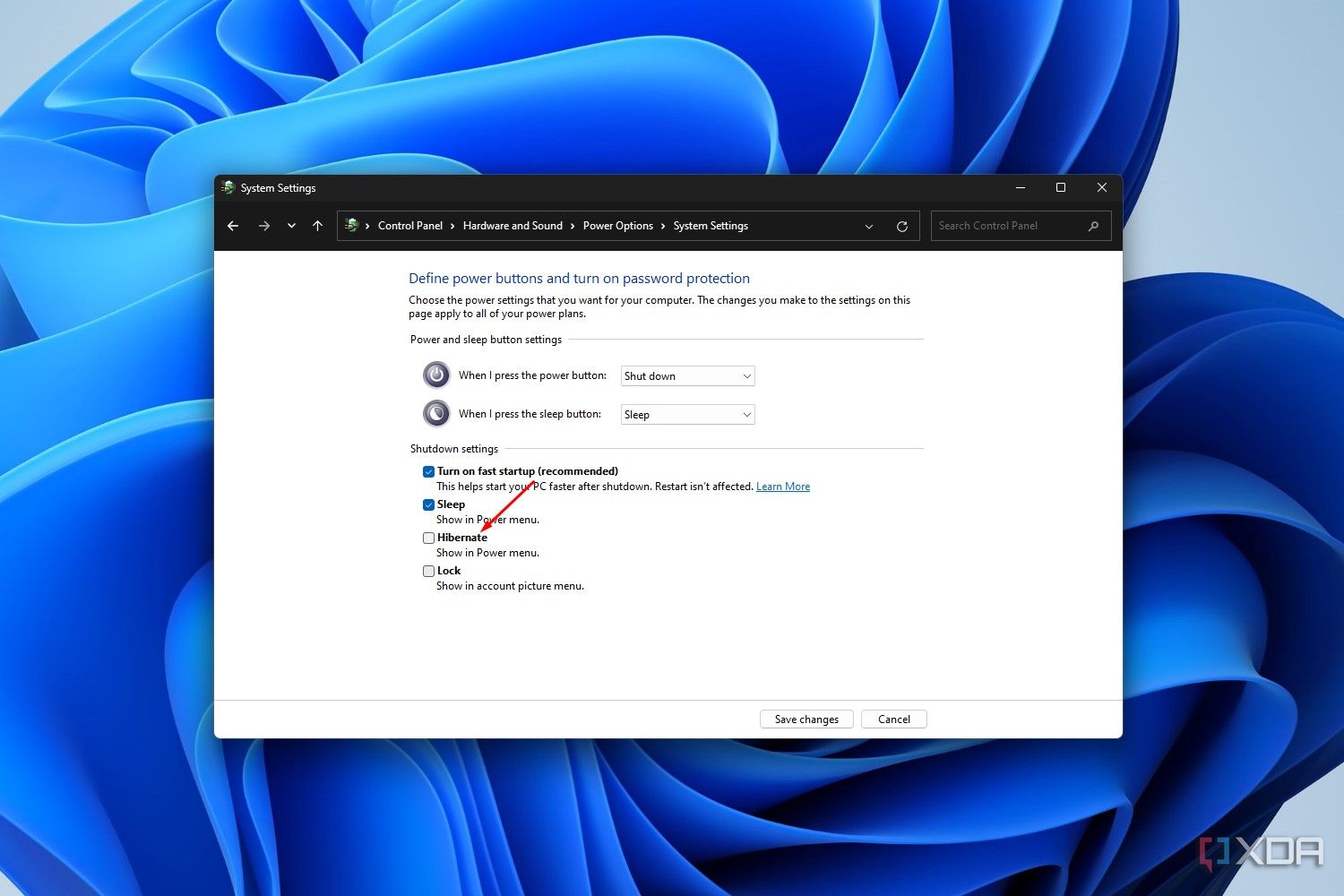
That’s all there is to it. The next time you click on the power menu in Windows 11, you’ll see the Hibernate option right above the Shut Down option. To disable Hibernate mode, follow the same steps above and just uncheck the Hibernate setting when you get to the Power Options menu.
How to enable hibernate mode in Windows 11 using Command Prompt
If you can’t see the hibernate option in the Power Options menu, the hibernation file is likely missing from Windows 11. This could happen for several reasons: Windows could delete the file if you’re running low on disk space, and certain system cleaning tools might accidentally remove it. System errors or file corruption can also lead to the hibernation file’s disappearance.
Whatever the case may be, you can quickly recreate the hibernation file in Windows 11 using the Command Prompt. Follow the steps below to do so:
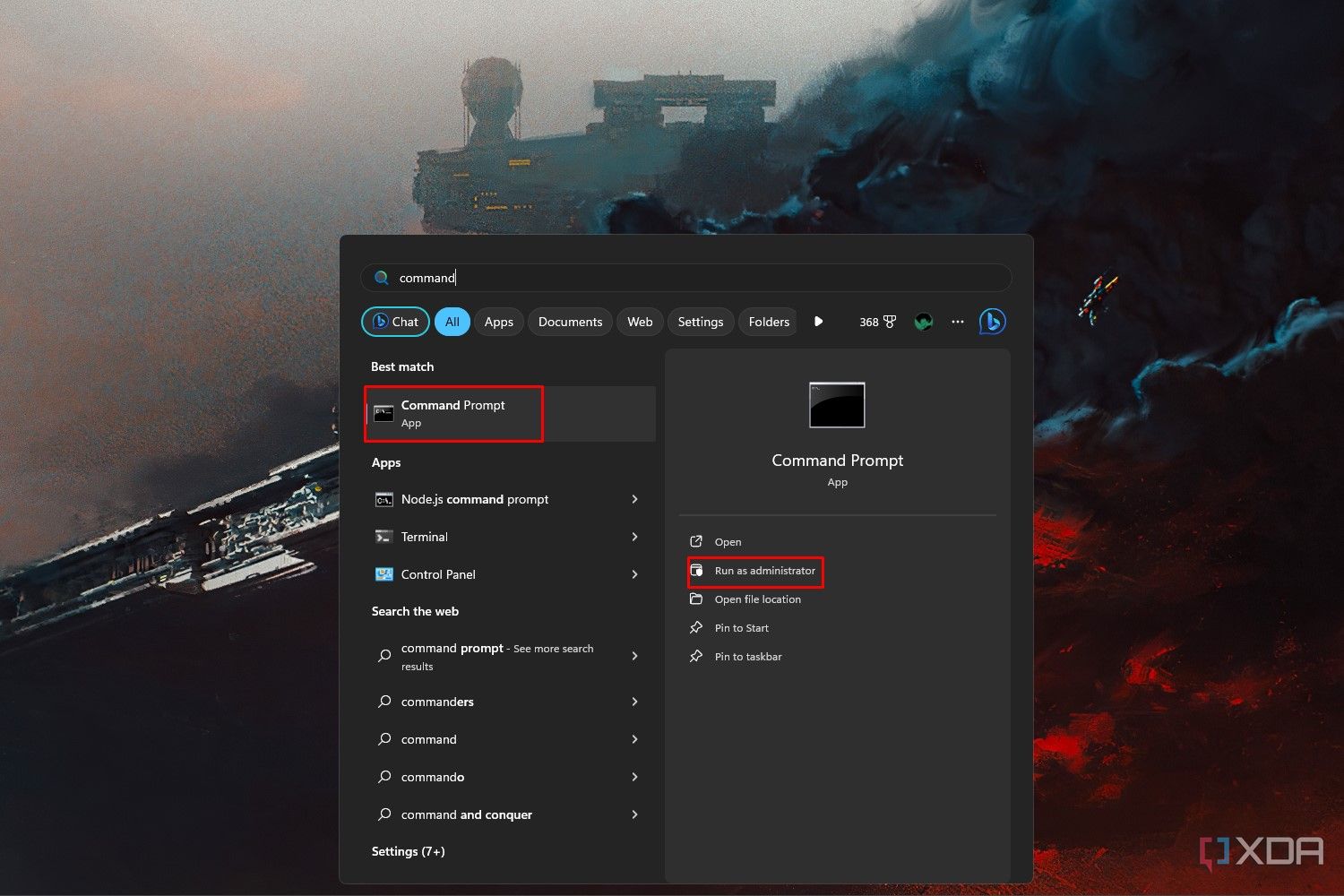
- Search for the Command Prompt app in the Start menu, and click Run as administrator.
- Type this command into the terminal and Enter on your keyboard to switch on hibernation mode:
powercfg /hibernate on - After entering the command above, you need to set the type of hibernation as well. We want to create a standard hibernation mode file, so type this command into the terminal and hit Enter on your keyboard:
powercfg /h /type full
The first command is used to enable hibernation mode and create the hibernation file, while the second one configures the type and size. Now, just click the power menu icon in the Start Menu, and you’ll find the Hibernate option right above the Shutdown option.
If you want to disable hibernation mode, you can delete the hibernation file by entering this command into the Command Prompt terminal:
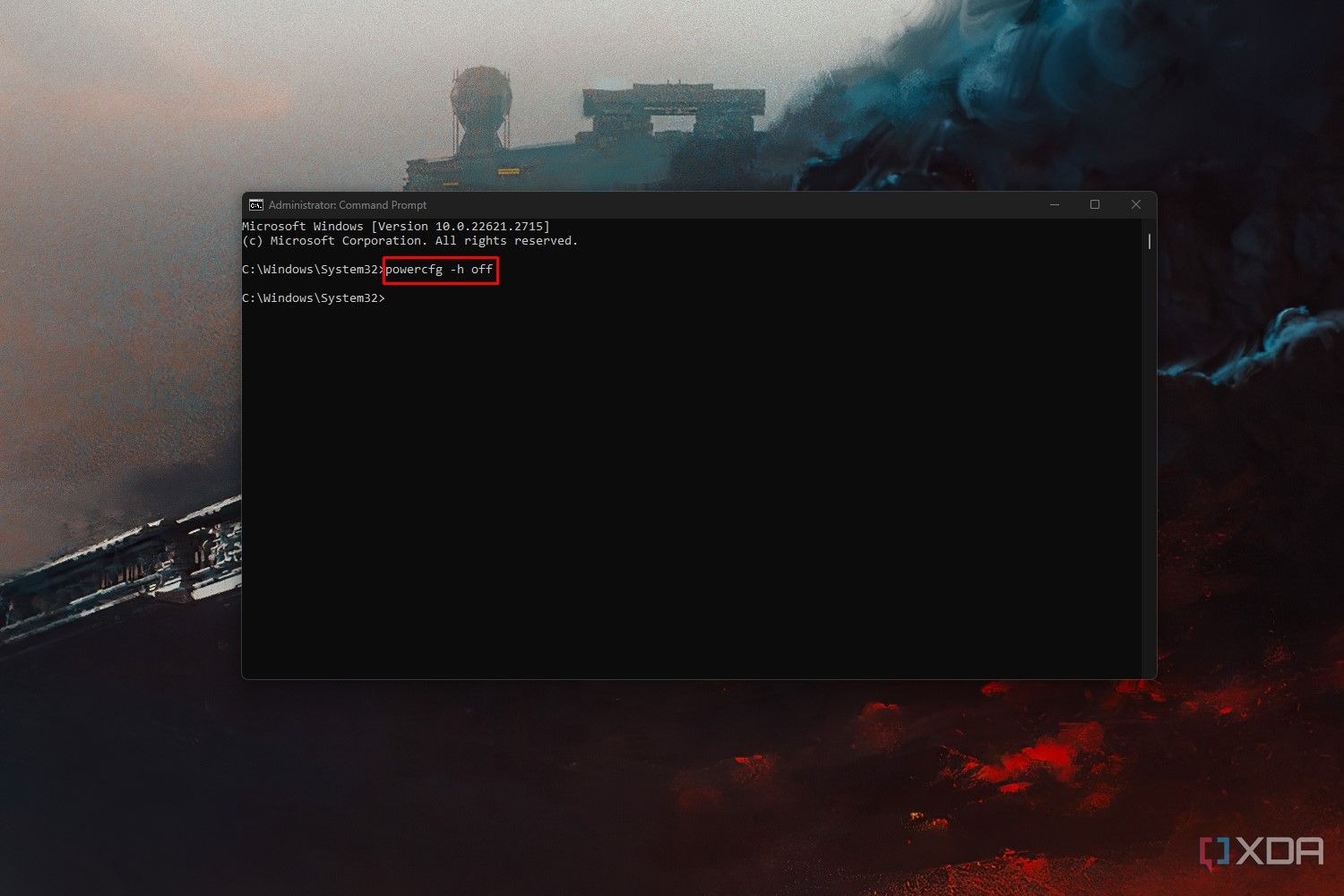
powercfg-h off
How to enable Hibernate mode in Windows 11 using Registry Editor
Another way of enabling hibernate mode is by tweaking the registry settings. This might be a bit advanced if you’re unfamiliar with the registry editor, but as long as you follow the steps properly, you’ll be fine.
- In the Windows 11 Start Menu, type Regedit into the search bar and select the Run as administrator.
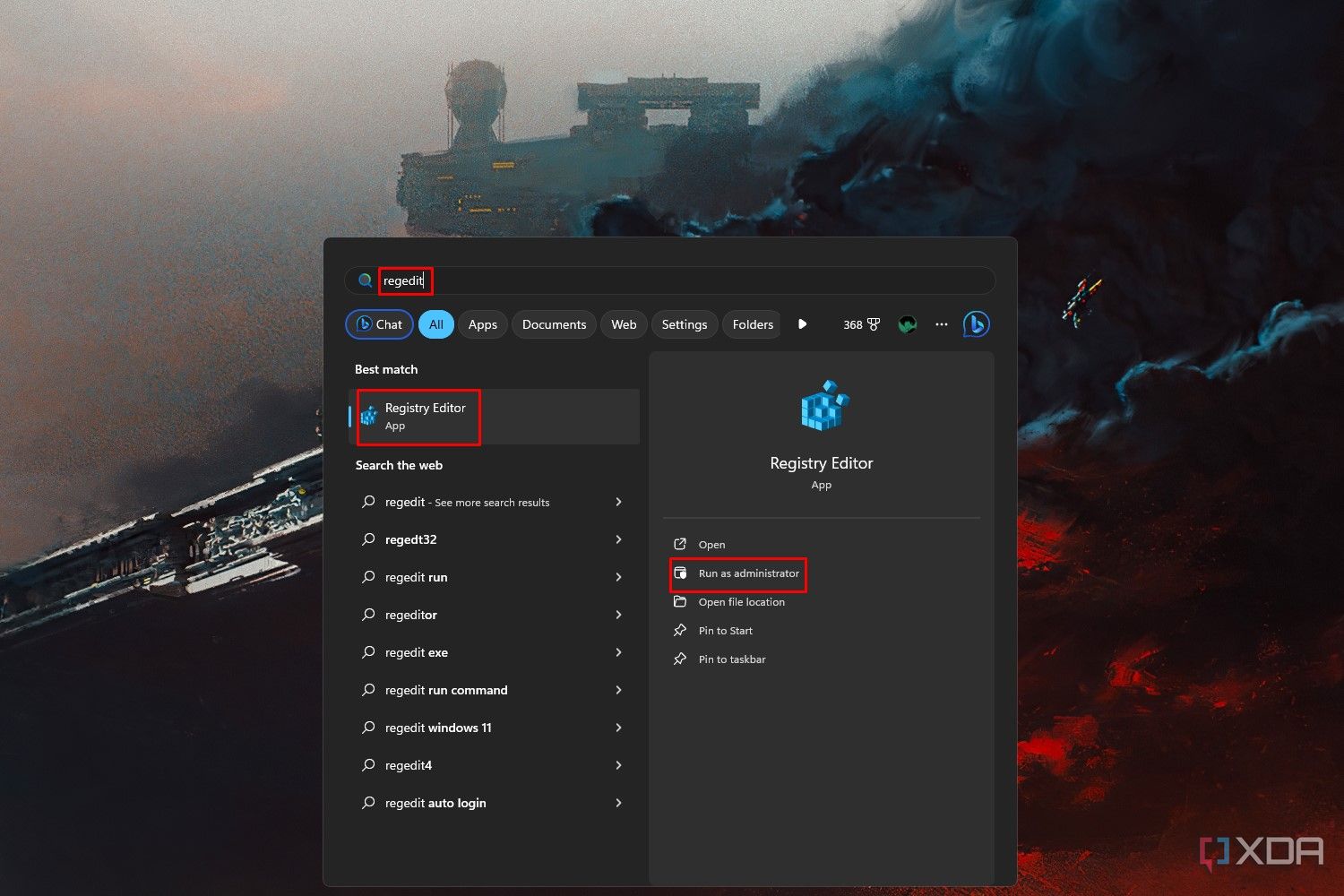
- When the Registry Editor launches, you’ll see an address bar in the top area that says Computer. Copy and paste this path into the address bar:
ComputerHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetC ontrolPower - In the right-hand area, look for the HibernateEableDefault option in the list of settings.
- Double-click the HibernateEableDefault option to open an edit window.
- Under the Value Data field, type 1 and click OK.
This simple registry edit will enable the Hibernation feature on your Windows 11 system. If you ever want to disable hibernation or reverse this edit, follow the steps above again and set the Value Data to 0.
Making the most of the power options in Windows 11
After you hibernate your PC, your screen will turn off, and all open programs or apps will be suspended. Like sleep mode, you can continue where you left off after you turn on your PC. While hibernate mode is inherently much slower than sleep mode, it is a helpful setting to have on hand for longer inactive periods. At the very least, it’s a feature that somehow manages to work better than the surprisingly bad Modern Standby feature.
** (Disclaimer: This video content is intended for educational and informational purposes only) **
More...